








Slide Show - Treating and Managing Ovarian Cancer
Your feedback is important to us! We will use your feedback to develop future areas of content about ovarian cancer which will help other patients, caregivers and families.






























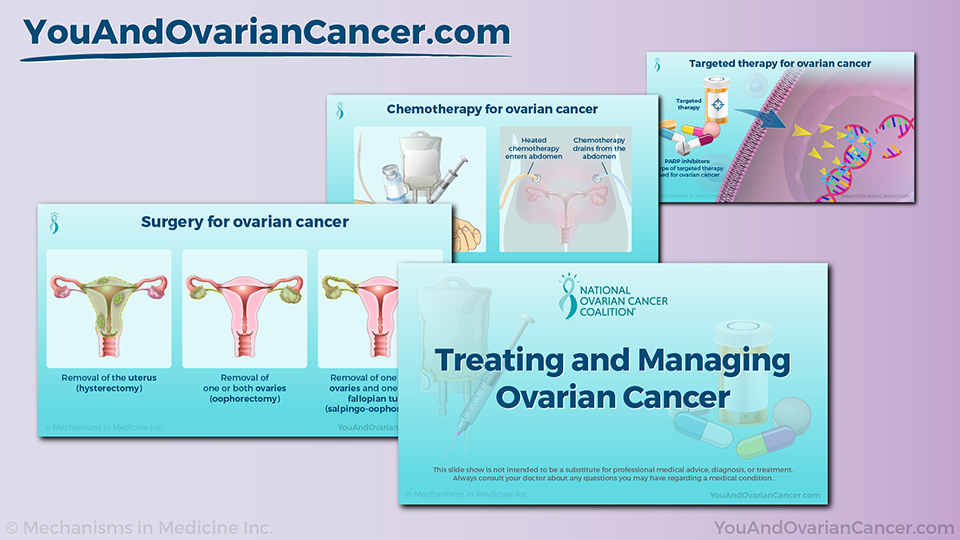
Treating and Managing Ovarian Cancer
*Please note: This slide show is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor about any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Customizing your ovarian cancer treatment plan
Your ovarian cancer treatment plan should be customized based on:
You and your doctor should share decisions about your treatment plan.
Consulting a specialist
A gynecologic oncologist specializes in caring for women with cancers of the reproductive organs.
Studies show that women with ovarian cancer have better outcomes when a gynecologic oncologist who does many surgeries performs their cancer surgery.
Ask your doctor for a referral to a gynecologic oncologist.
Goals of surgery for ovarian cancer
For ovarian cancer the goals of surgery are:
Surgery for ovarian cancer
The type of surgery performed will depend on factors such as:
Surgery for ovarian cancer
Surgery may include removing the uterus, one or both ovaries, or one or both fallopian tubes.
Surgery for ovarian cancer
If you want to have children in the future, ask your doctor if fertility-sparing surgery is an option for you.
Ovarian cancer surgery and menopause
Menopause is the time of life when your menstrual cycles stop. For many women, natural menopause occurs in their early 50s.
If you have surgery to remove both ovaries before you've entered natural menopause, the surgery will cause you to enter menopause right away. This is often called surgical menopause.
Ovarian cancer surgery and menopause
Common symptoms of menopause include:
Menopause also increases your risk for bone loss in the future.
Before you have surgery, ask your doctor what can be done to treat symptoms of menopause and protect your bone health.
Chemotherapy for ovarian cancer
Chemotherapy, or chemo, uses anticancer drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemo may be given:
Chemotherapy for ovarian cancer
Patients with ovarian cancer most often receive combination chemo with two or more drugs that attack the cancer in different ways.
Chemo for ovarian cancer is usually injected into a vein through an IV.
In select cases, it may be heated and injected into the abdomen either during or after surgery. This is called "hot chemo", or HIPEC.
Targeted therapy for ovarian cancer
Cancer starts when abnormal cells grow and multiply without stopping. Targeted therapy uses drugs that attack these abnormal cells to stop the cancer from growing or spreading.
PARP inhibitors, which we will discuss shortly, are a type of targeted therapy, called maintenance therapy, used to treat ovarian cancer.
Other treatment options for ovarian cancer
Clinical trials
Clinical trials are studies of new drugs or procedures in people. They are used to test whether new medications are safe and more effective than existing ones.
By enrolling in a clinical trial, you may be able to get a new treatment for ovarian cancer before it's generally available.
Ask your doctor if enrolling in an ovarian cancer clinical trial is right for you.
Maintenance treatment
After you complete chemo, your doctor may prescribe maintenance treatment to prevent or delay a return of your cancer based on your surgery findings or specific testing of your tumor.
For example, studies show that when PARP inhibitors are given as maintenance treatment, they delay recurrence in some patients. They may also reduce the risk that cancer will return.
Your doctor also will want to do periodic blood tests and scans to make sure there is no evidence of disease.
Managing side effects
Most treatments for ovarian cancer have side effects that can affect your body, your emotions, and your mental state.
Talk with your healthcare team about any side effects you're having. They can work with you to find ways to relieve and manage your side effects.
Getting support for ovarian cancer
It’s also important to get social and emotional support for your well-being. Consider talking to a counselor or joining a support group to help you through this time.
Your healthcare team, friends, family members, and others can help you cope with your emotions and guide you on this journey.
References
Your feedback is important to us! We will use your feedback to develop future areas of content about ovarian cancer which will help other patients, caregivers and families.















This educational activity has been developed by the National Ovarian Cancer Coalition in collaboration with Mechanisms in Medicine Inc.
This activity is supported by educational grants from:
Alkermes plc, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Clovis Oncology, Inc., Eisai Inc., Foundation Medicine, Inc., Genentech, a Member of the Roche Group, GSK, ImmunoGen, Inc., Merck & Co, Inc., Novartis, Novocure Inc., Pfizer, Inc.
Copyright © Mechanisms in Medicine Inc. All rights reserved. Mechanisms in Medicine Inc. does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
This website is part of the Animated Patient® series developed by Mechanisms in Medicine Inc., to provide highly visual formats of learning for patients to improve their understanding, make informed decisions, and partner with their healthcare professionals for optimal outcomes.